CR-39 for Nuclear Particle Track Detection
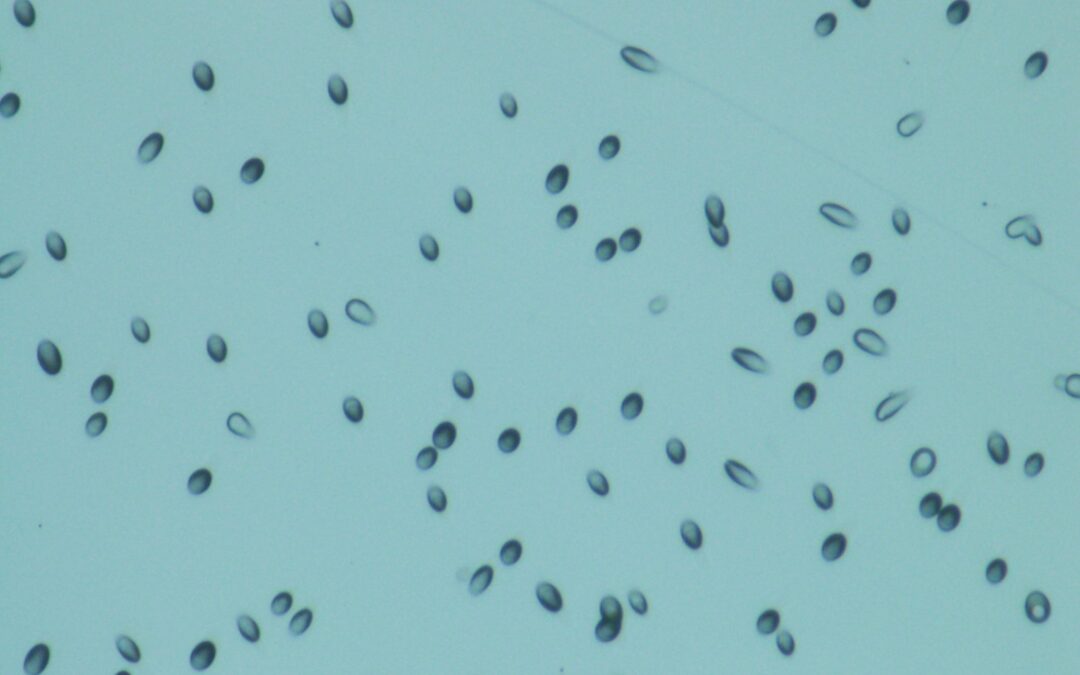
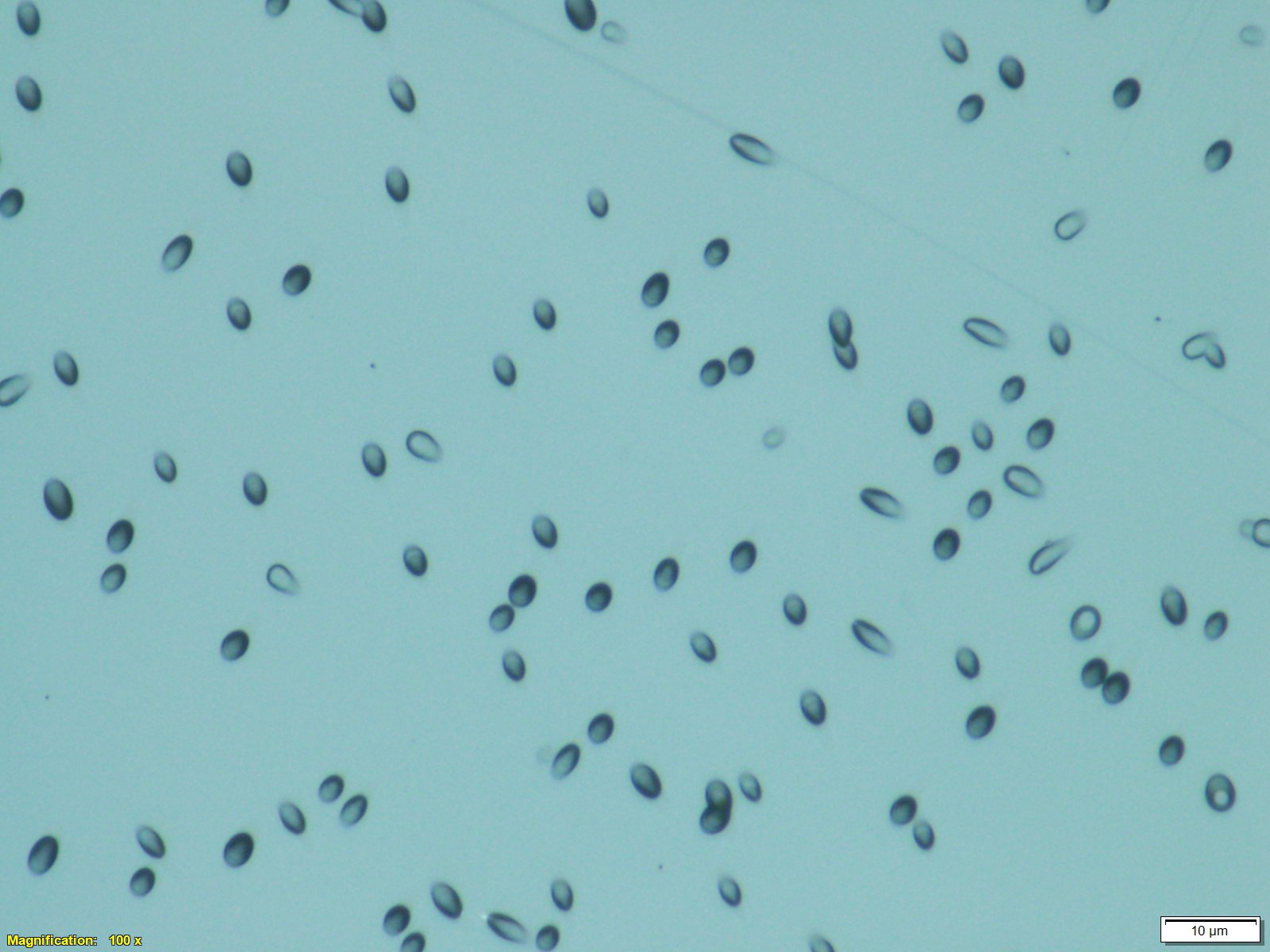
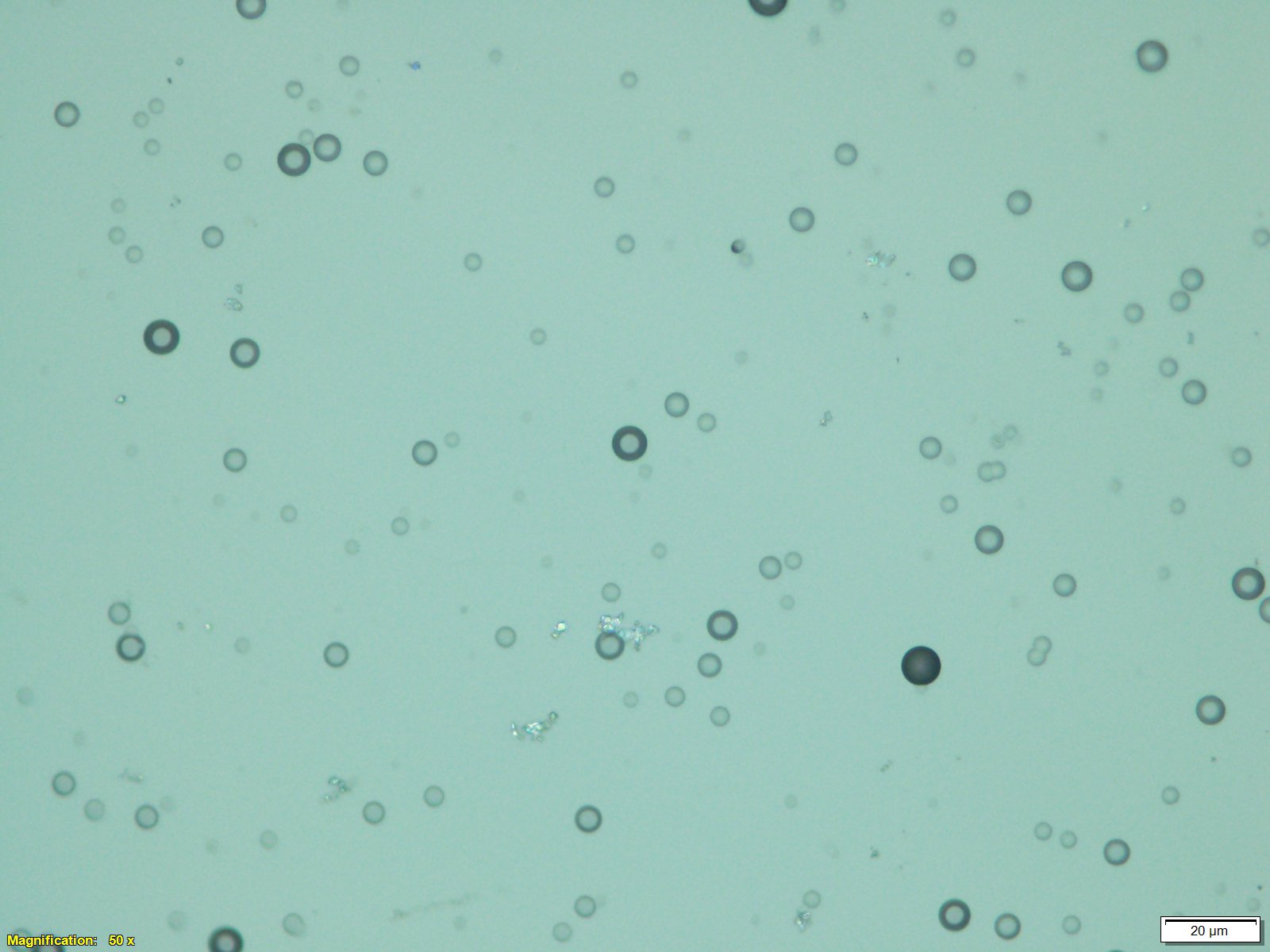
The thermoset polymer, CR-39, is used in nuclear particle tracing and calorimetry as a solid state nuclear track detector (SSNTD). When a high energy particle impacts the polymer it breaks bonds and allows for preferential etching during post-exposure processing. These etched tracks can then be observed and characterized under a microscope.
CR-39 is sensitive to many particles such as energetic protons, alpha-particles and heavier ions, and fast neutrons. Thermal/epithermal neutrons can be detected by doping CR-39 with boron to produce the 10B(n,a)7Li reaction and subsequent alpha-particle detection.
This SSNTD has a wide variety of applications of radiation measurement, including home radon detection, dosimetry, and is a less visceral display of radiation damage for educators.
Click here for more information for best practice for the use of CR-39.
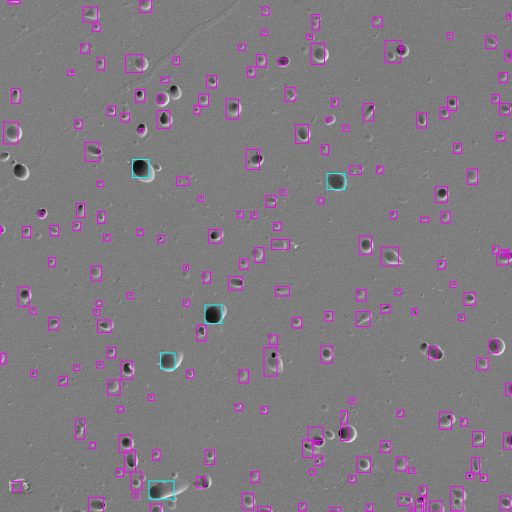
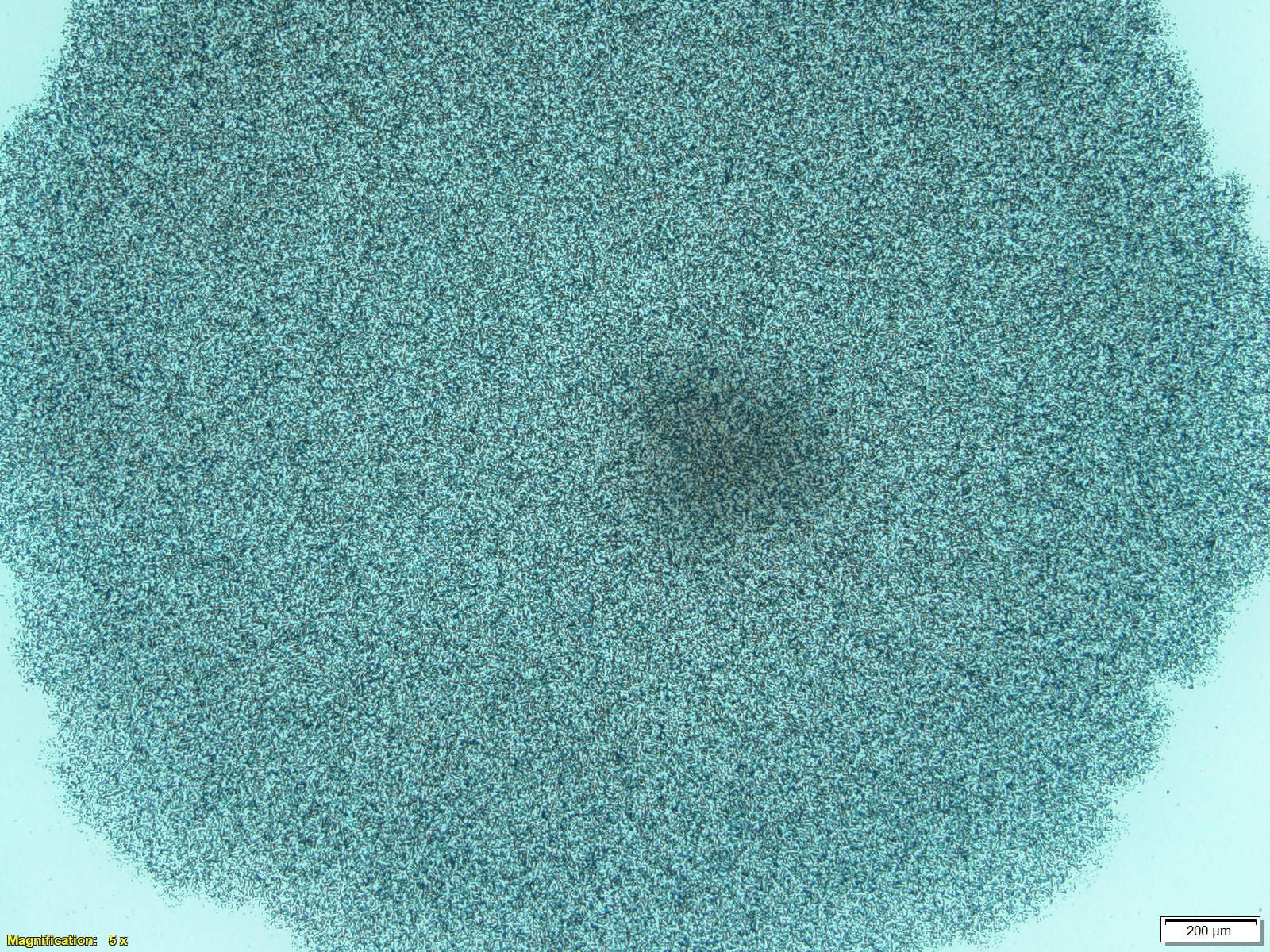
Click here for electron microscope web application image. This image is of our CR-39 exposed to Am-241 alpha particles. Notice the direction of impact and depth of penetration. Here is the same image with AI labeling of features. Here is an image of U-238 fission fragment tracks boxed in cyan.
SEM image of 14 MeV neutron-induced proton-recoil (magenta) and U-238 fission fragment (cyan) with AI detection.